
As a UX Designer, you have a range of techniques available to you, and it’s up to you to choose which of these techniques are appropriate.
Mastering when and how best to use these techniques should be the goal of every UX Designer.
UX Process Overview
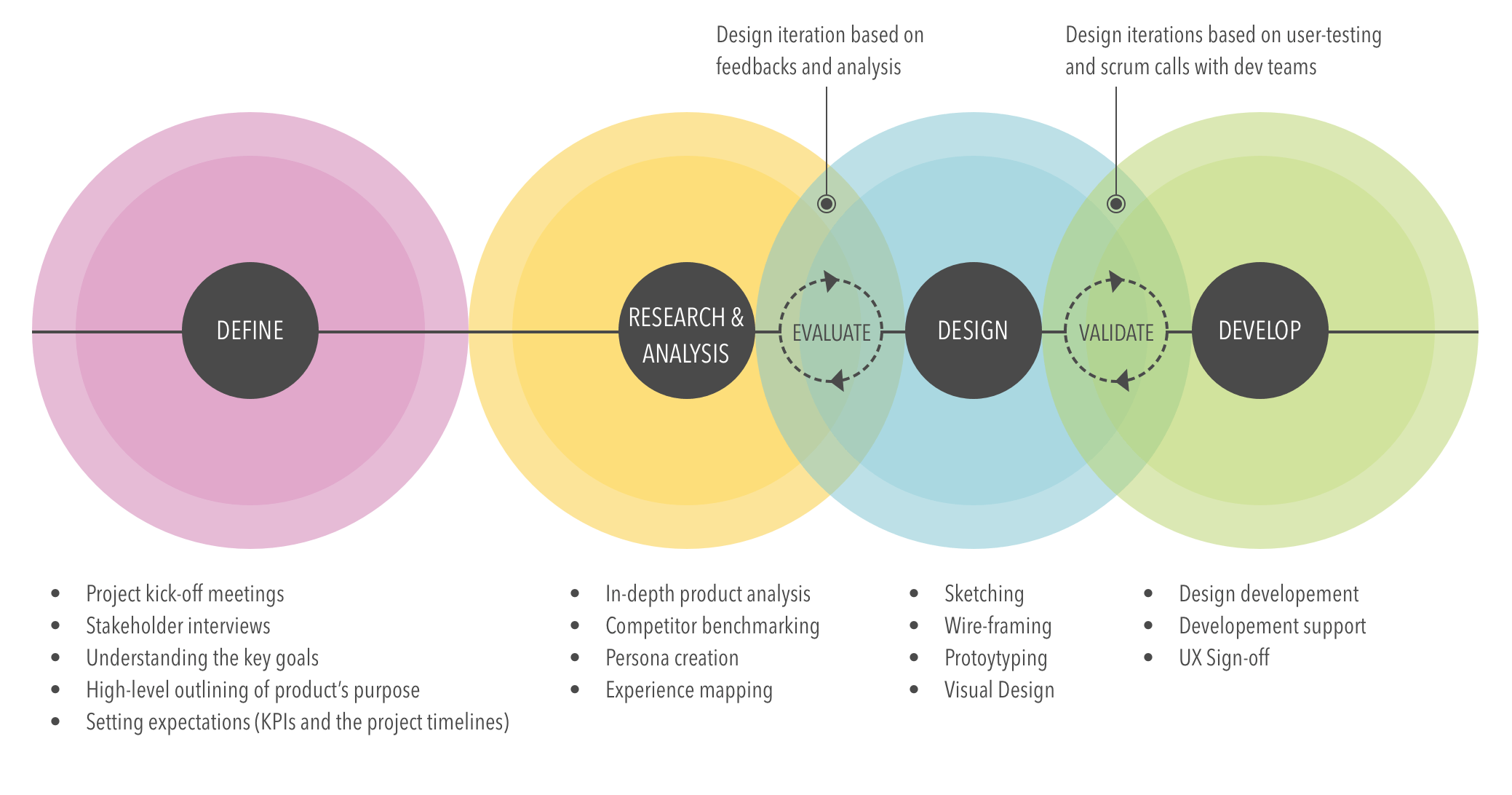
At its core, every UX process should consist of the following key phases:
-
- Strategy—Strategy is important from the outset because it articulates the brand, guiding principles, and long-term vision of an organisation. The strategy underpinning a UX project will shape the goals of the project—what the organisation is hoping to achieve with the project, how its success should be measured, and what priority it should have in the grand scheme of things.
- Research—Often referred to as the Discovery phase, the Research phase is probably the most variable between projects. Complex projects will comprise significant user and competitor research activities, while small startup websites may skip all research activities other than some informal interviews and a survey. In many people’s eyes, the Research phase is key to creating an informed user experience, however it is also the phase most often skipped—especially by proponents of a “Lean UX” approach.
- Analysis—The aim of the Analysis phase is to draw insights from data collected during the Research phase. Capturing, organising and making inferences from the “what” can help UX Designers begin to understand the “why”. Communicating the designer’s understanding back to end-users helps to confirm that any assumptions being made are valid.
- Design—The Design phase of a UX project is collaborative (involving input and ideas from different people) and iterative(meaning that it cycles back upon itself to validate ideas and assumptions). Building on the user feedback loop established in previous phases, the premise of the Design phase is to put ideas in front of users, get their feedback, refine them, and repeat. These ideas may be represented by paper prototypes, interactive wireframes, or semi-functioning prototypes, all deliberately created in low-fidelity to delay any conversation relating to graphic identity, branding or visual details.
- Production—The Production phase is where the high-fidelity design is fleshed out, content and digital assets are created, and a high-fidelity version of the product is validated with stakeholders and end-users through user testing sessions. The role of the UX Designer shifts from creating and validating ideas to collaborating with developers to guide and champion the vision.


